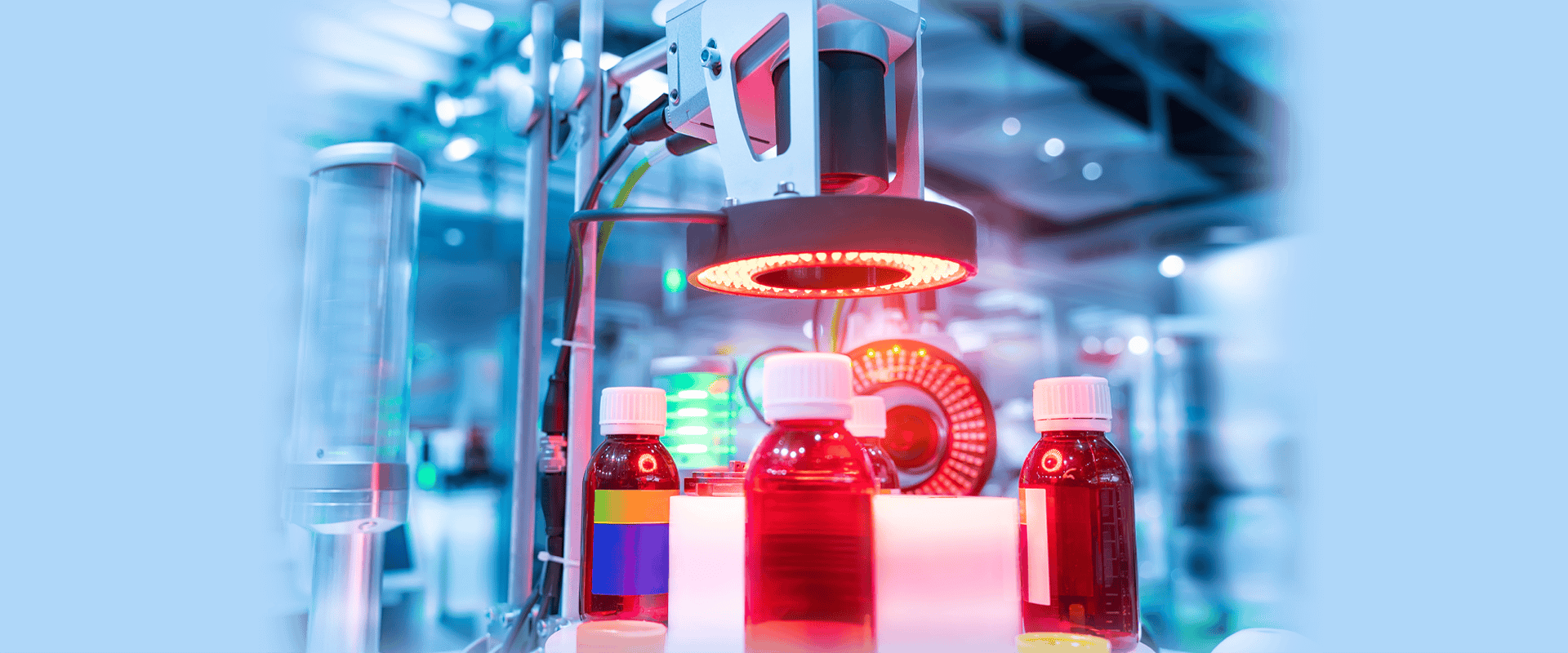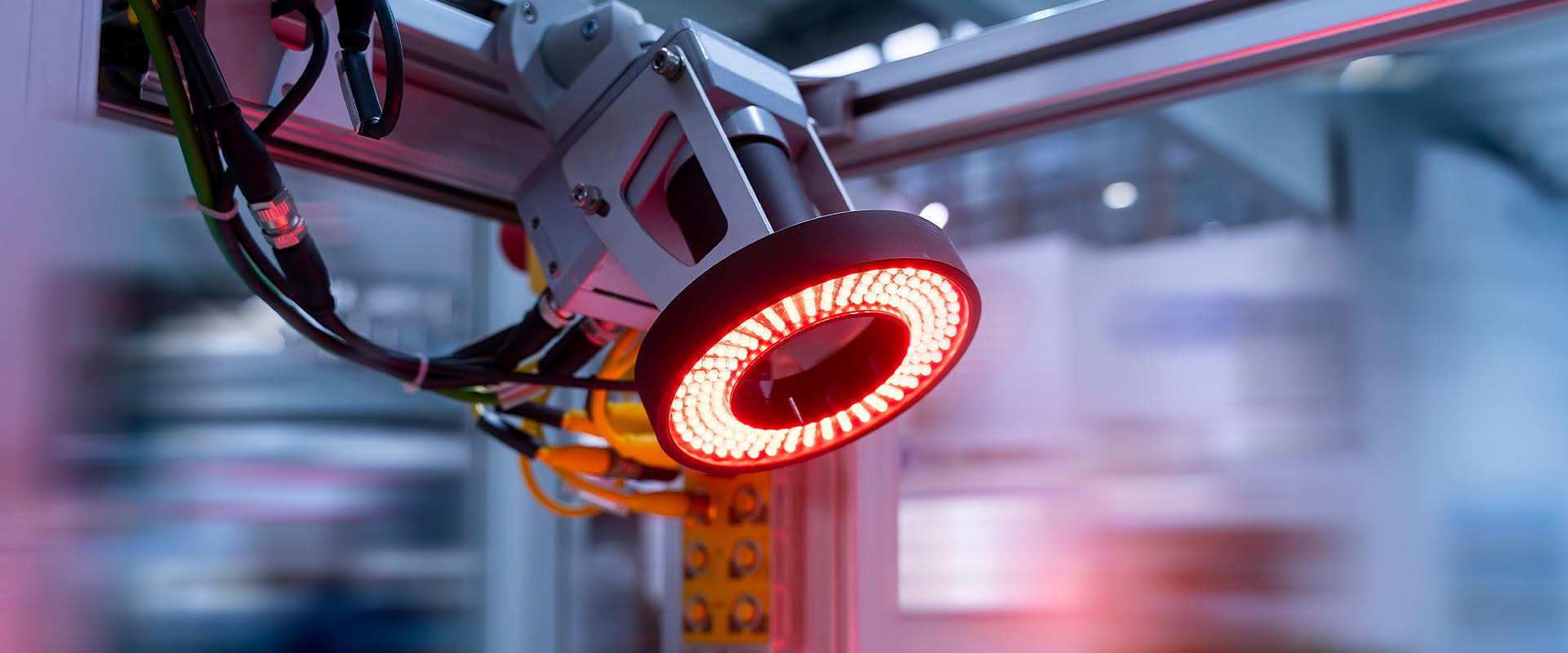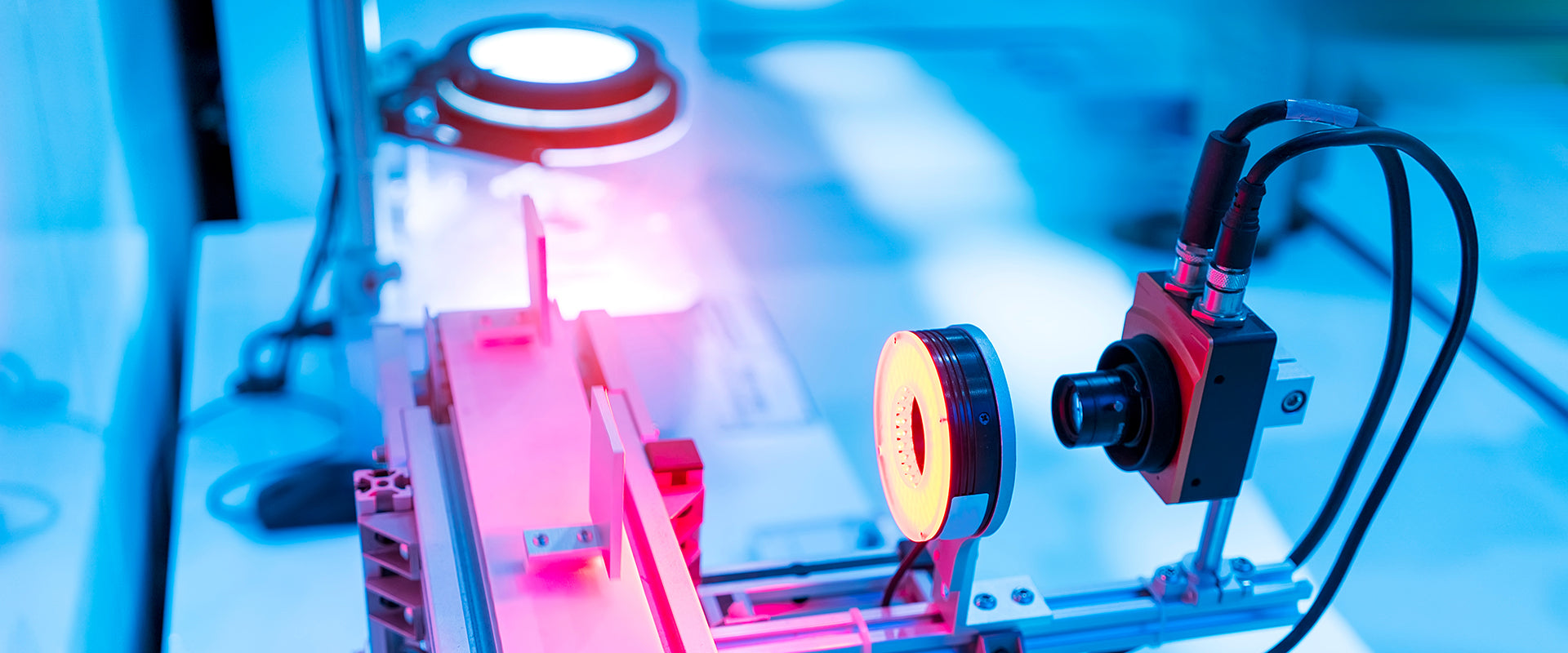
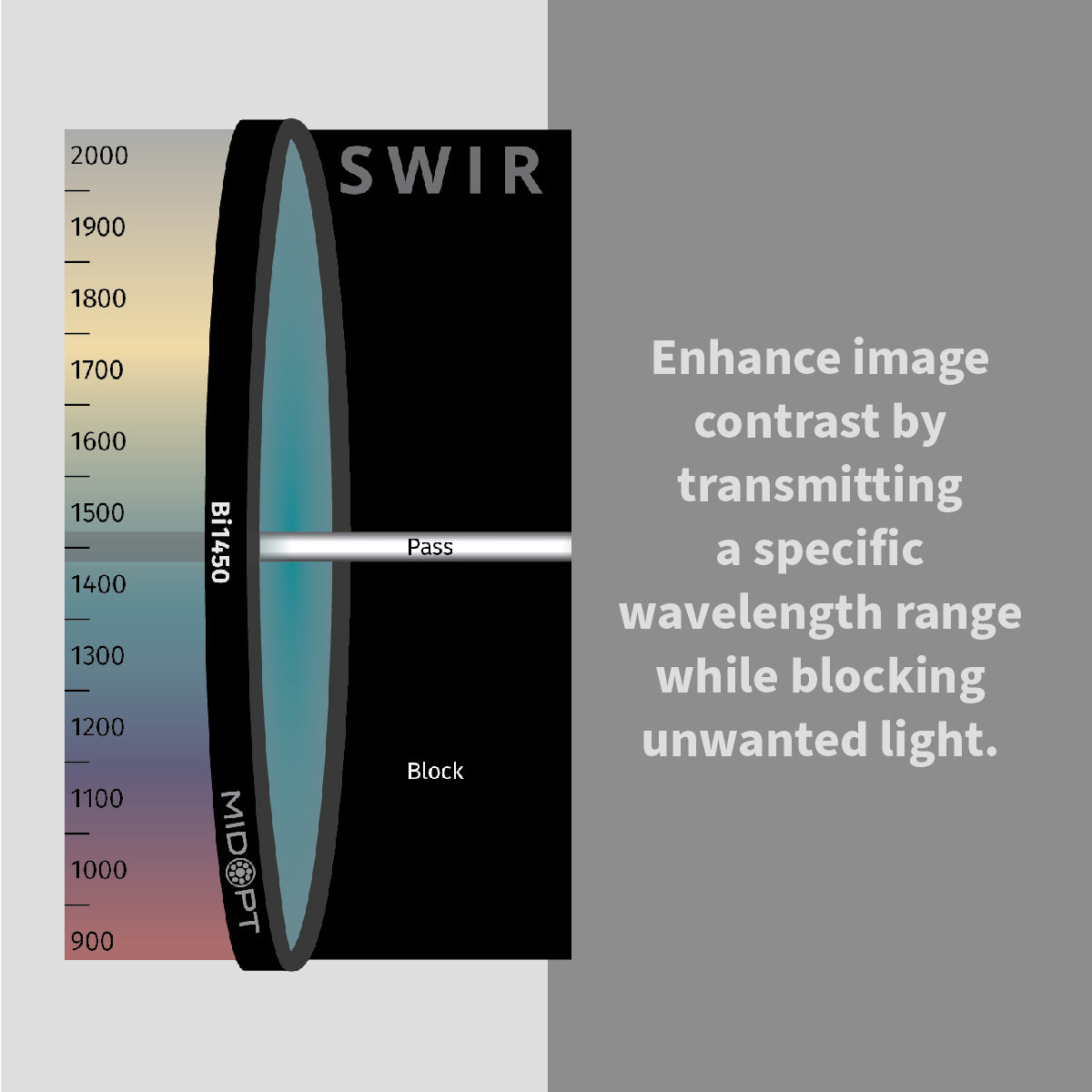
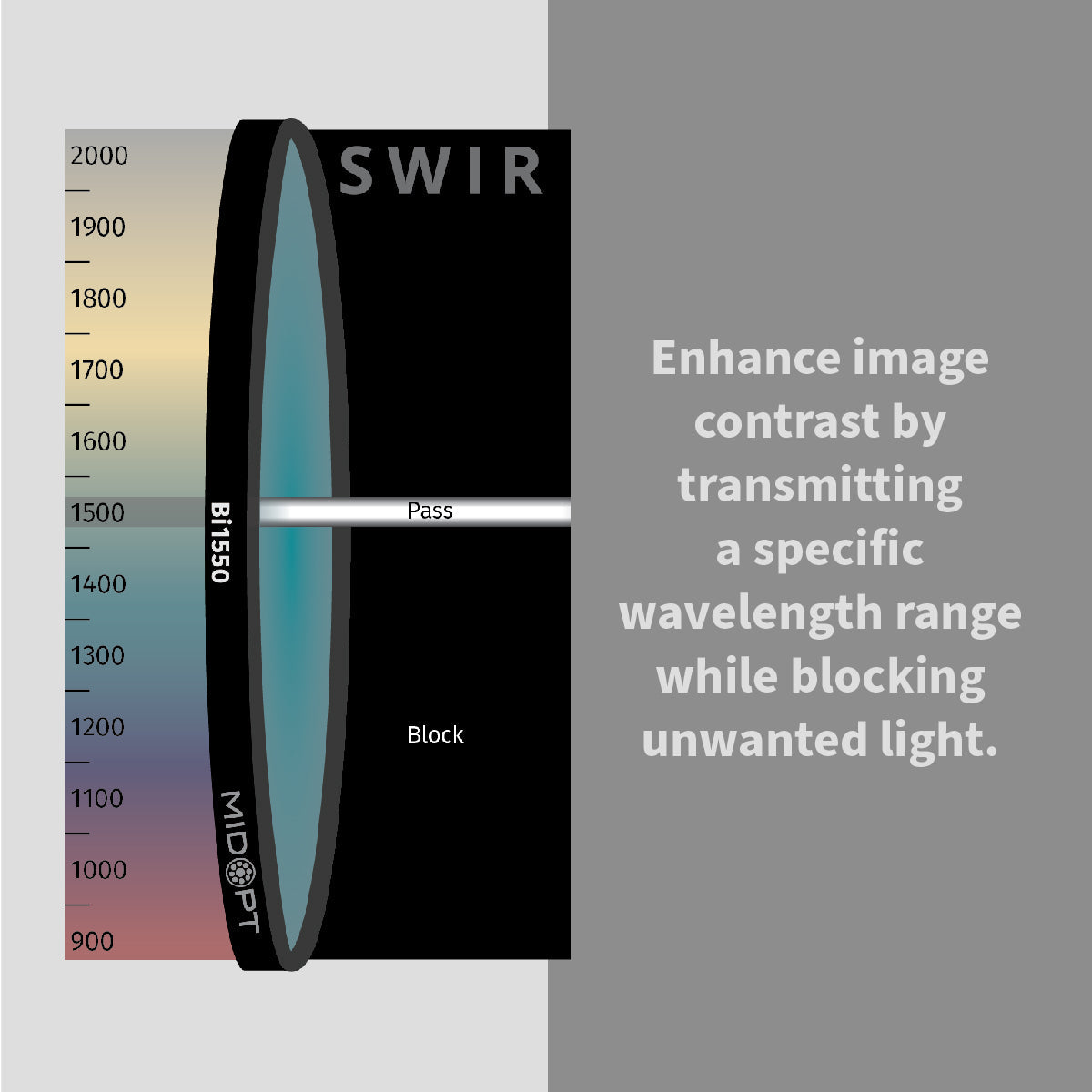
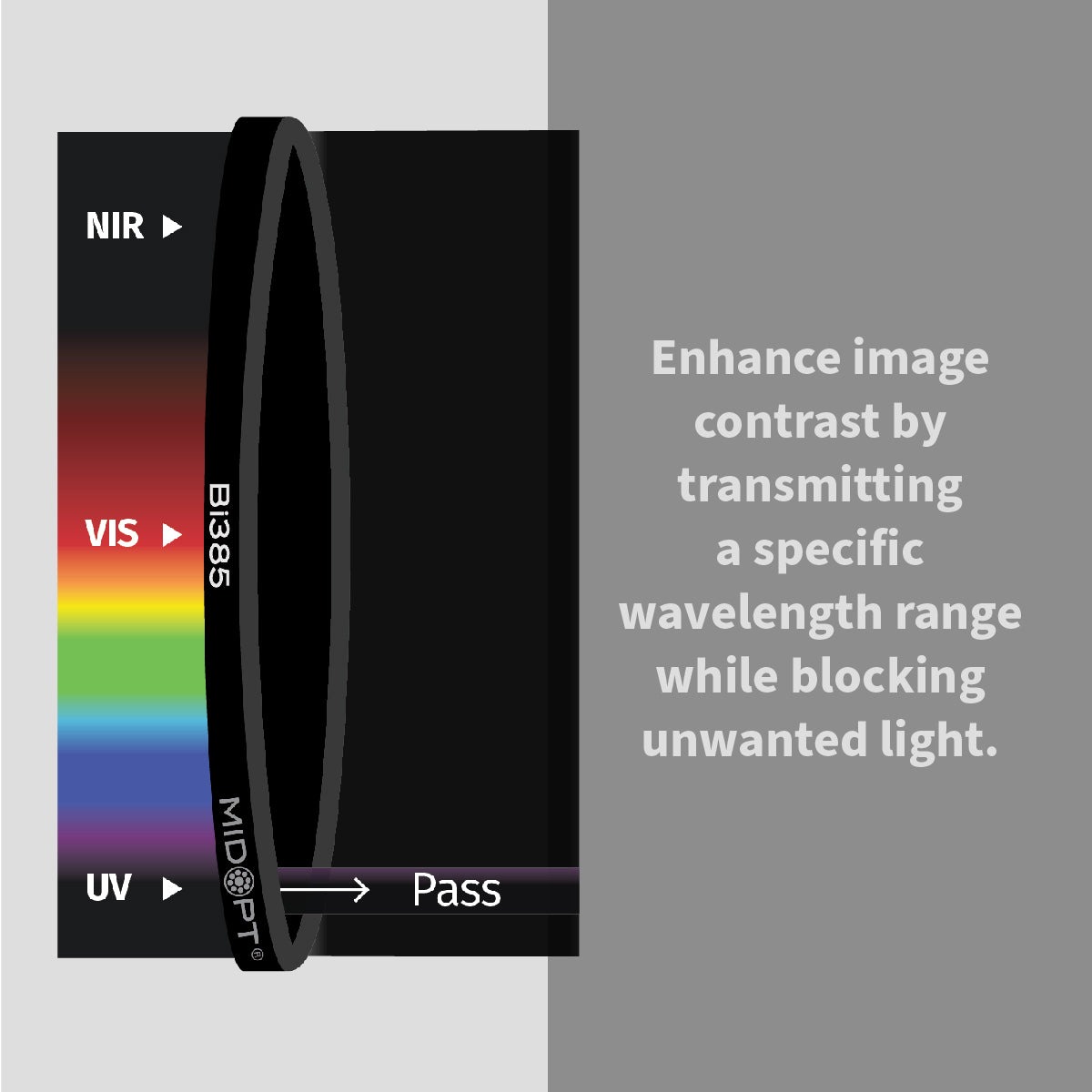
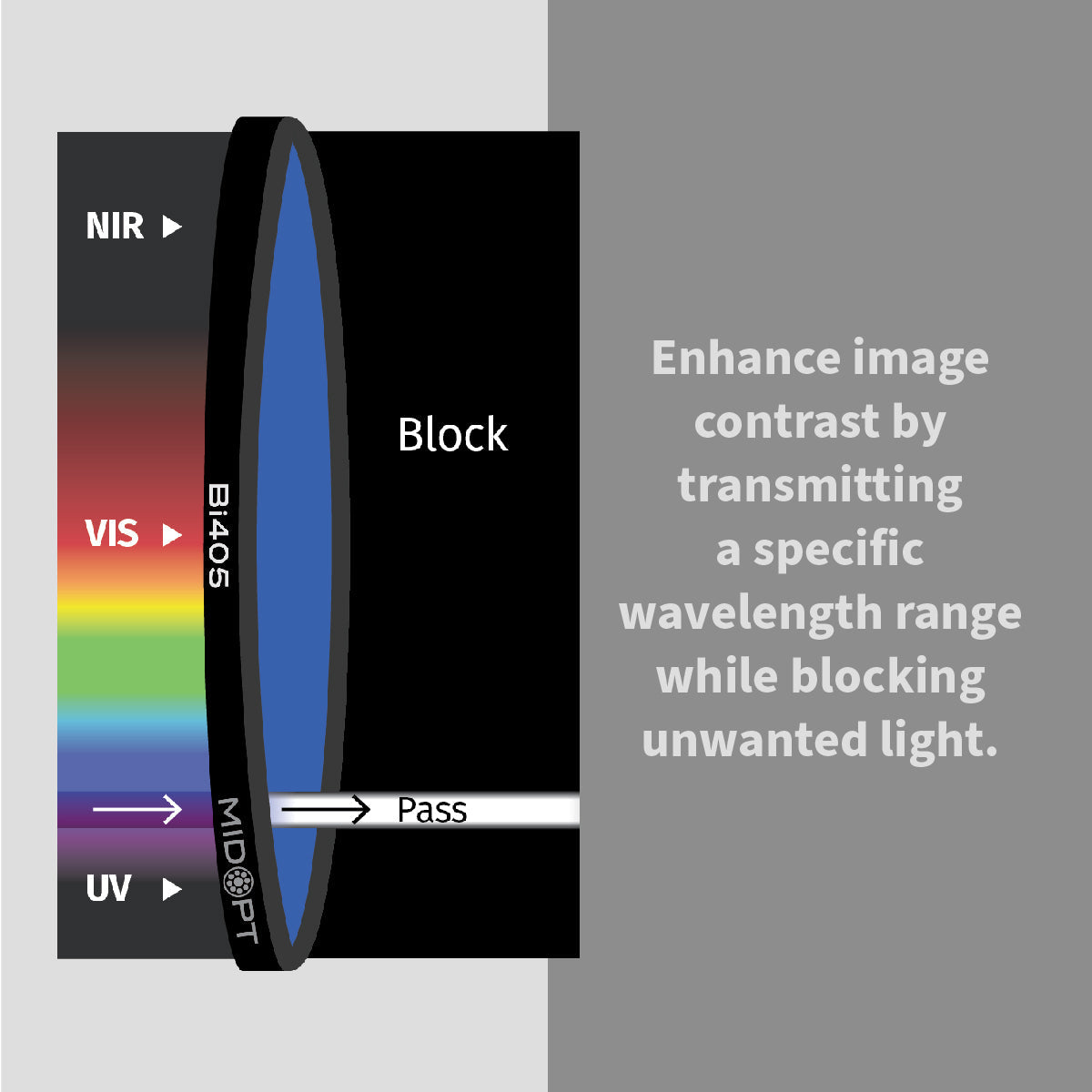
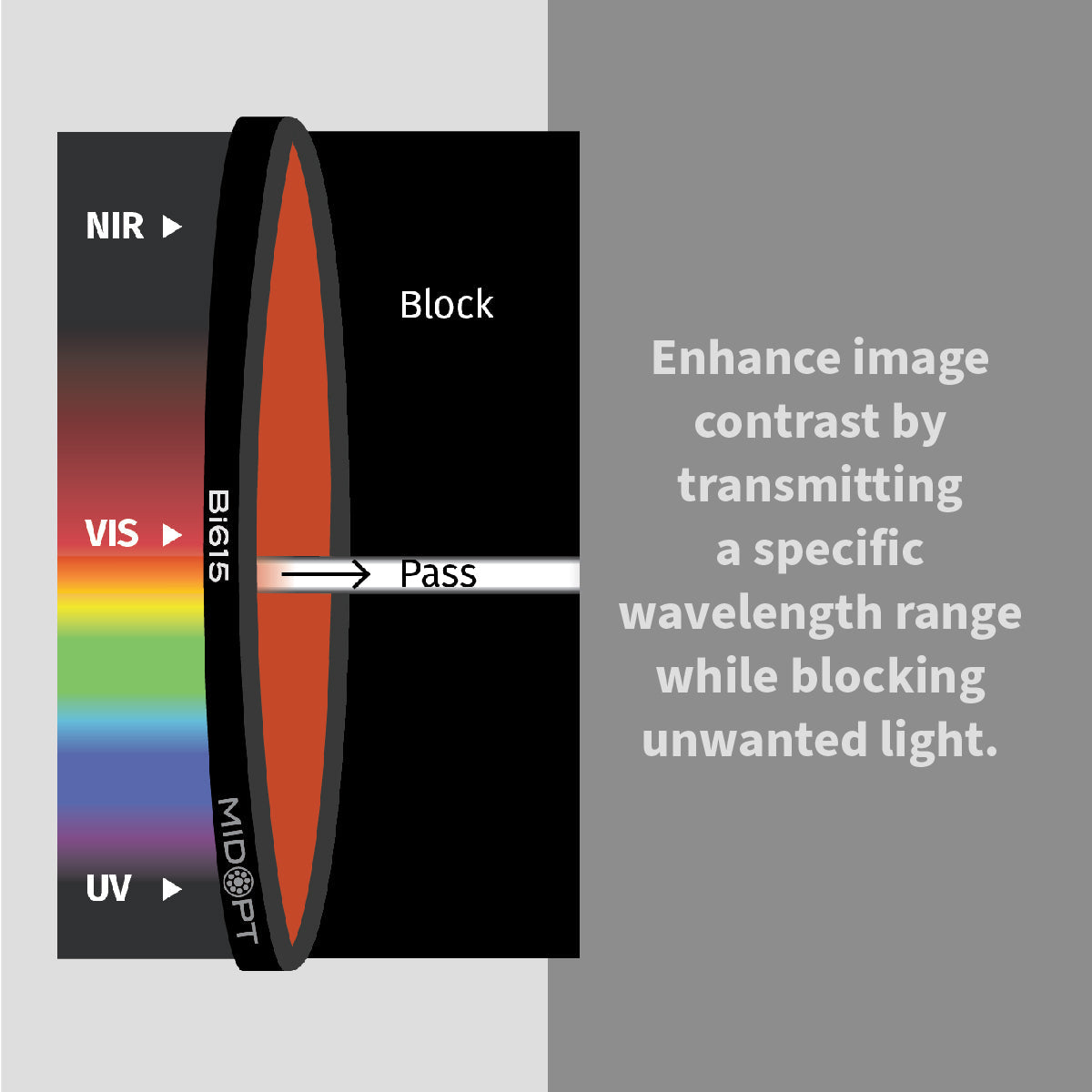
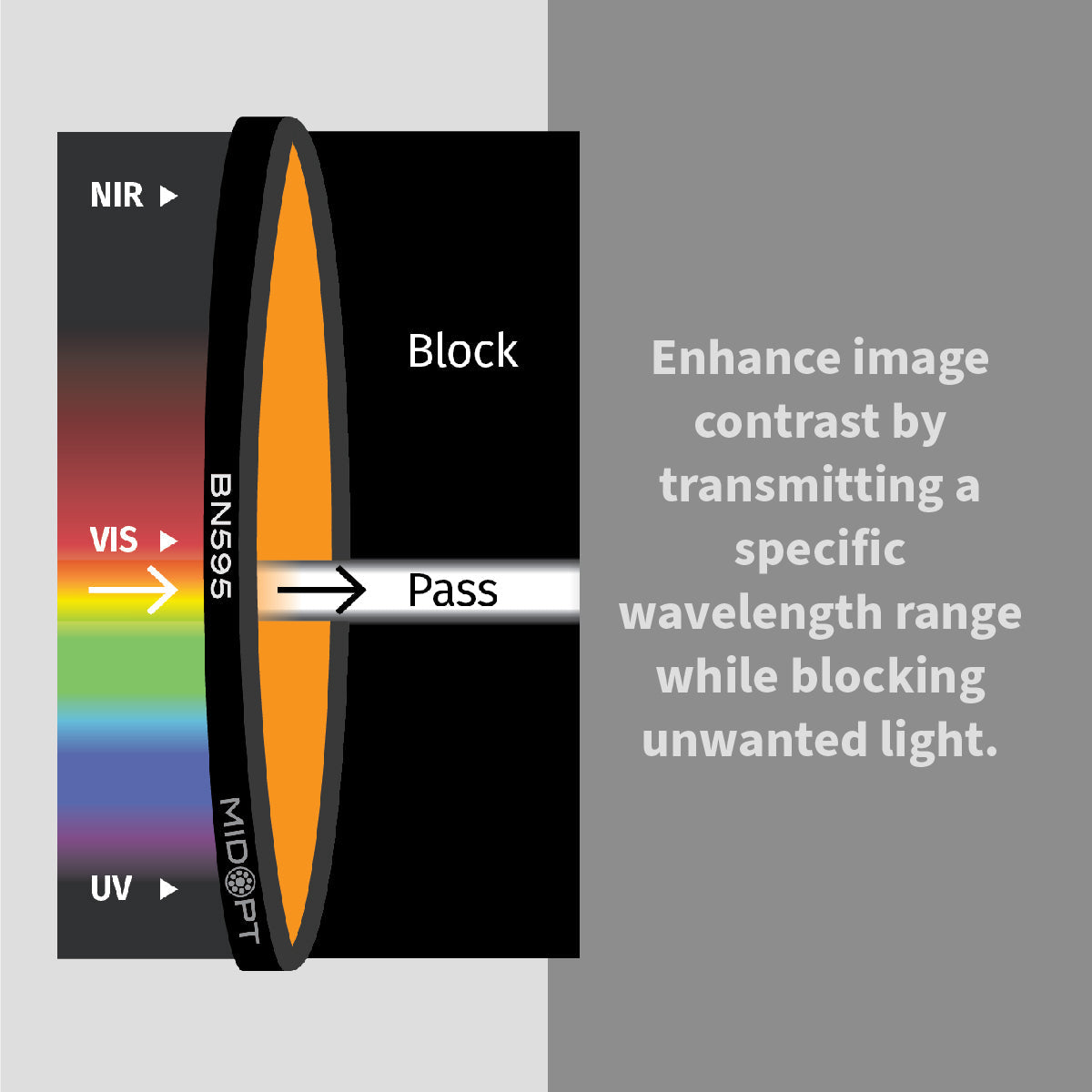
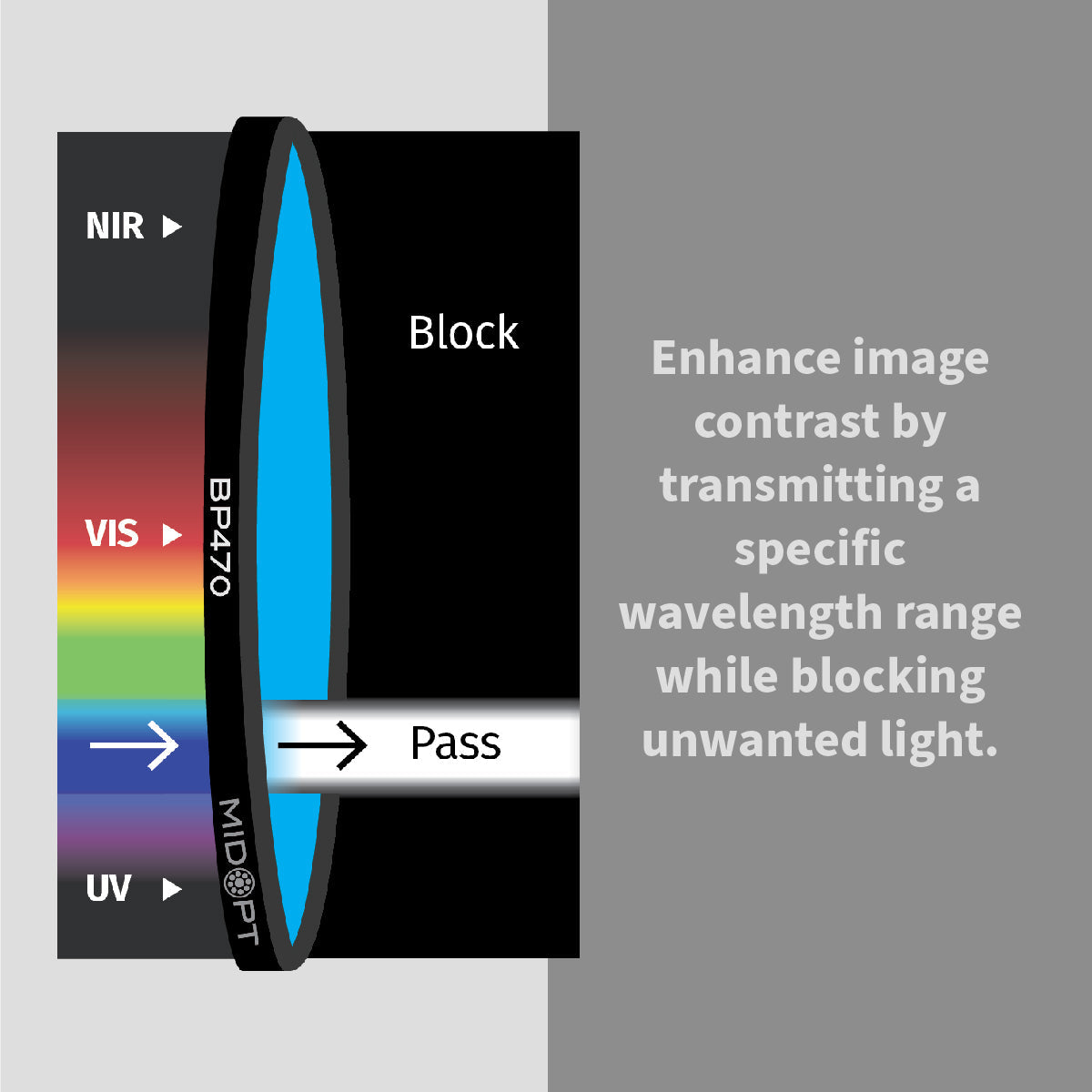
In high-performance industrial environments, image accuracy determines inspection reliability. Machine vision bandpass filters are engineered to isolate specific wavelengths of light, eliminating unwanted spectral noise and enhancing image contrast in automated inspection systems.

This 2026 optimization guide explains how lighting and filters work together, when to use each, and how to design the right combination for industrial inspection applications.

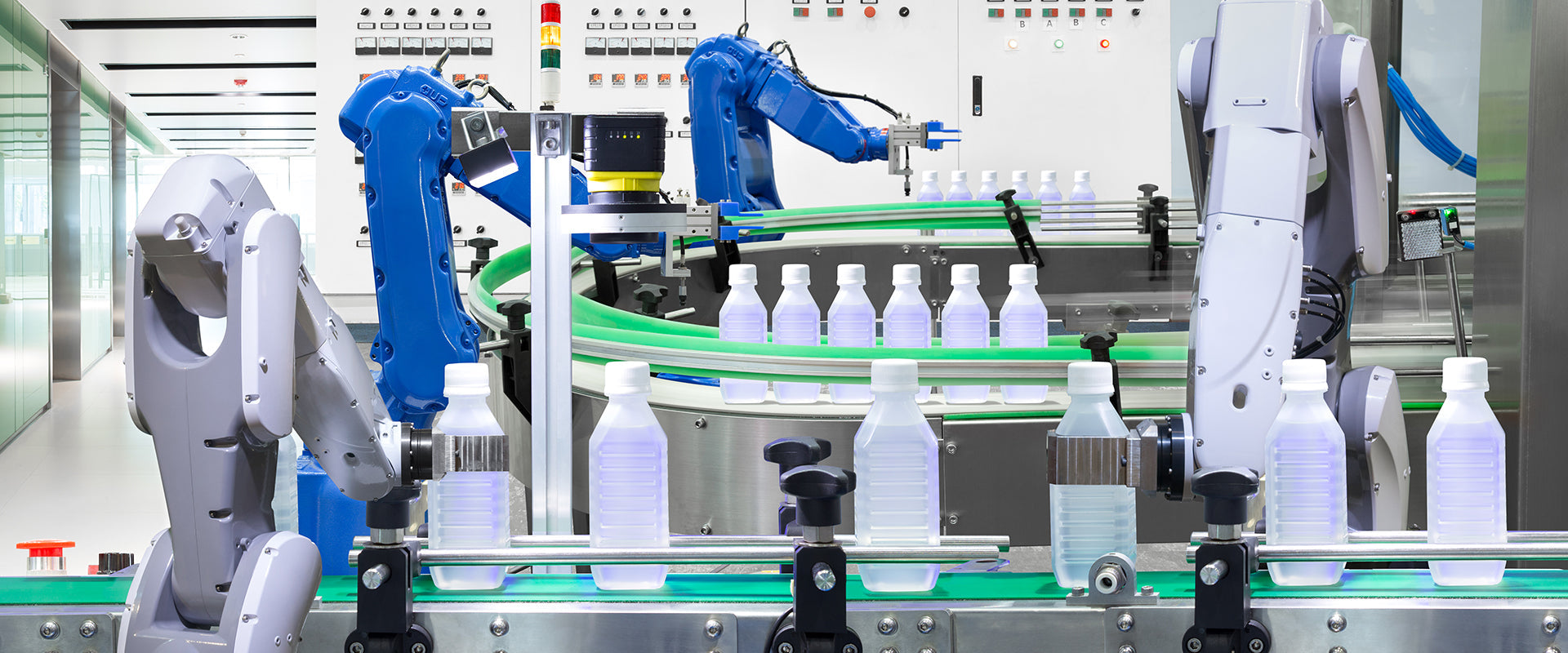
Selecting the right industrial inspection camera is one of the most critical decisions in machine vision system design. The wrong choice can result in missed defects, false rejects, reduced production speed, and costly downtime.

Designing a high-performance machine vision system requires more than selecting a camera and turning on a light. In industrial inspection environments, image quality determines measurement accuracy, defect detection reliability, and production efficiency.

In machine vision, lighting isn’t just about brightness – it’s about control. One of the biggest challenges in capturing consistent, high-quality images is glare and reflections from shiny or specular surfaces. These unwanted highlights can obscure critical details, confuse algorithms and lower inspection accuracy. This is where polarized lighting plays a powerful role, offering a practical solution to suppress glare and reveal hidden detail in reflective environments.

Selecting the right lens is critical to the success of any machine vision system. While cameras and lighting often get the spotlight, the lens ultimately determines image clarity, field of view, magnification and inspection accuracy. Two of the most common lens types used in industrial imaging are fixed focal lenses and zoom lenses, each with distinct advantages depending on the application.

In machine vision systems, optical filters play a critical role in controlling light, improving contrast and enhancing image accuracy. But even the best filter can't perform as intended if it's not mounted correctly. Mounting solutions for machine vision filters are a foundational yet often overlooked part of system design, directly affecting alignment, stability, repeatability and overall image quality.

In machine vision applications, accuracy is everything. Even small optical errors can lead to failed inspections, incorrect measurements or reduced system reliability. One of the most common optical challenges is lens distortion. Understanding what lens distortion is and how to minimize it is critical when designing precision vision systems for inspection, measurement and automation.

When it comes to machine vision, one of the most influential lighting variables is lighting angle, which directly impacts contrast, edge definition, surface visibility and defect detection. Selecting the correct lighting angle can mean the difference between a reliable inspection system and inconsistent results.

Machine vision cameras are the backbone of any inspection, measurement or automation system. But as sensor technology, interfaces and processing demands evolve, older cameras can quietly become a bottleneck, limiting performance, accuracy and scalability. If your system is struggling to keep up, it may be time for an upgrade.

Achieving accurate, repeatable results depends on far more than just selecting the right camera or lens. One of the most overlooked components in many imaging systems is the optical filter. When properly selected, filters dramatically improve image quality, reduce variability and ensure consistent performance across changing environments.

In machine vision and industrial inspection, understanding the difference between infrared vs thermal imaging is essential for choosing the right technology. Although the two are often confused or used interchangeably, they rely on different wavelength regions, serve different purposes and are optimized for specific types of applications.

Machine vision is an essential technology for automation, quality control, robotics and industrial inspection. But with so many types of machine vision systems available today, it can be challenging to determine which configuration is right for your application.

Choosing the right lens for a machine vision system involves more than focal length, resolution and working distance. The lens mount, the mechanical interface between the camera and lens, is one of the most important factors in ensuring proper imaging performance. The mount not only affects compatibility, but also impacts back focal distance, sensor coverage, optical stability and the overall footprint of the system.

Lighting is one of the most influential factors in machine vision performance. The right illumination can dramatically improve contrast, reduce noise and stabilize inspection results, while the wrong setup can cause missed defects, blurry images or inconsistent measurements.
























































 Lighting
Lighting






